Chapitres
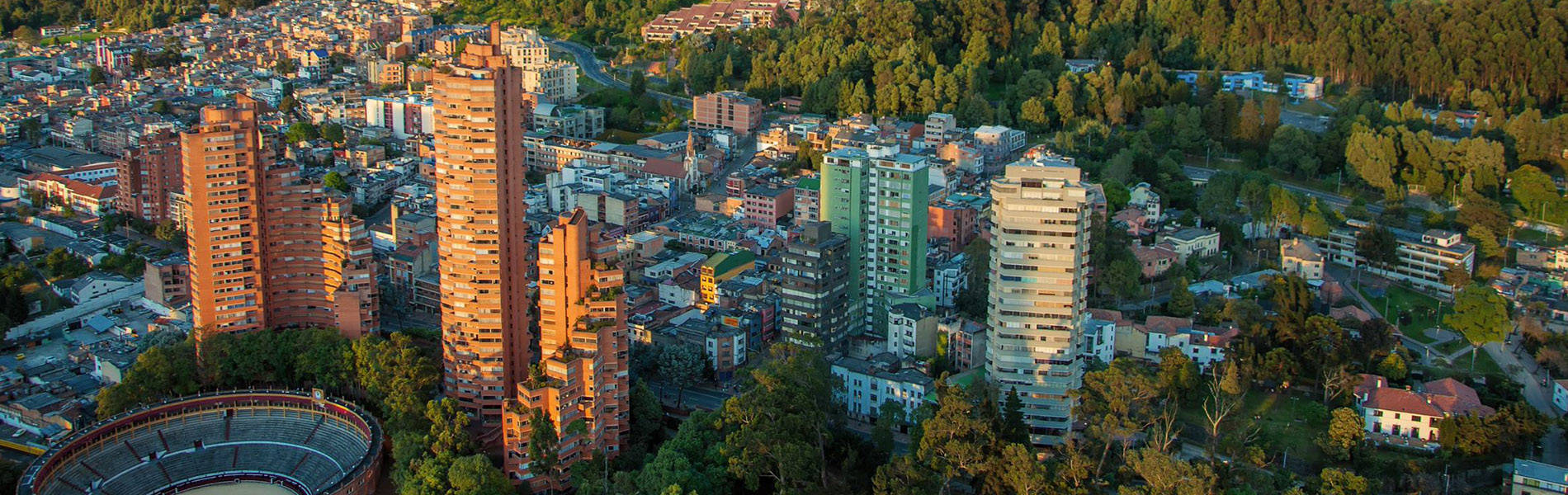
Colombia’s solid macroeconomic institutional setting, grounded on a rules-based fiscal framework, a flexible exchange rate, and a modern inflation-targeting regime, has been the cornerstone of its macroeconomic stability. Yet, the pace of economic growth has been slowing. Colombia has significant potential to enhance its contribution to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth by increasing productivity - which has remained stagnant for decades - and further diversifying and expanding its exports.
In terms of regional and international finance and partnerships to catalyse international resources, Colombia’s 2023-26 National Strategy for International Co‑operation secures USD 96 million for climate action, environmental justice, and the inclusion of the migrant population from bilateral donors and multilateral institutions. Initiatives like “Colombia + Competitiva” promote financial inclusion for micro, small and medium-sized enterprises, complemented by the World Bank Credit Project to drive sustainable transformation in agriculture. Collaboration with the French Development Agency is advancing electric vehicle mobility while ongoing negotiations with the IDB involve a credit facility backed by CIF resources, targeting decarbonisation, and accelerating inclusive energy transition. Preparation for the Fourth International Conference on Financing for Development underscores Colombia’s commitment, with its focus on a USD 4.5 billion Socio-ecological Transition Portfolio for biodiversity conservation, climate change mitigation, renewable energy, and sustainable rural development.
Source: The World Bank, OECD
Indicateurs clés
- Surface
- 1,138,910 km2
- Population
- 52,321,152 (2023)
- Type de gouvernement
- presidential republic
- Langues
- Spanish (official) 98.9%, indigenous 1%, Portuguese 0.1%; 65 indigenous languages exist (2023 est.)
- PIB
- $363.49 billion (2023)
- Taux de croissance
- 0.6% (2023)
- HDI
- 91
- Capitale
- Bogota
Indicateurs macroéconomiques
The economy will grow by 1.8% in 2024, with a gradual recovery to 2.7% in 2025 and 2.9% in 2026. Investment will continue recovering as financial conditions ease, though uncertainty will keep it below pre-pandemic levels. Consumption will grow moderately and export growth will remain solid. Inflation will continue to decline slowly, given high price indexation, returning to the 3% target by end-2026. Vulnerabilities from increasingly large fiscal and current account deficits are the main risks.
Monetary policy easing should continue cautiously. Given high planned fiscal deficits, which do not leave margin for risks, and recent revenue shortfalls, fiscal prudence and compliance with the fiscal rule is required. In the medium term, reducing budget rigidities and a comprehensive tax reform are needed to rebalance the tax burden from corporate to personal income, reduce tax expenditures, simplify the tax system, and tackle tax evasion.
Source: OECD
IMF Statistics:
| Subject descriptor | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
All Items, Consumer price index (CPI), Period average, percent change Percent (Units) |
11.729 |
6.602 |
4.913 |
3.471 |
3.037 |
|
Current account balance (credit less debit), Percent of GDP Percent (Units) |
-2.261 |
-1.741 |
-2.297 |
-2.572 |
-2.819 |
|
Current account balance (credit less debit), US dollar US dollar (Billions) |
-8.283 |
-7.29 |
-10.063 |
-11.887 |
-13.592 |
|
Exports of goods and services, Volume, Free on board (FOB), Percent change Percent (Units) |
2.222 |
2.243 |
0.342 |
1.638 |
1.963 |
|
Gross domestic product (GDP), Constant prices, Percent change Percent (Units) |
0.712 |
1.598 |
2.523 |
2.272 |
2.5 |
|
Gross domestic product (GDP), Current prices, Per capita, US dollar US dollar (Units) |
7015.002 |
7947.824 |
8249.219 |
8644.307 |
8961.047 |
|
Gross domestic product (GDP), Current prices, US dollar US dollar (Billions) |
366.292 |
418.818 |
438.121 |
462.251 |
482.176 |
|
Imports of goods and services, Volume, Cost insurance freight (CIF), Percent change Percent (Units) |
-12.419 |
2.81 |
5.555 |
5.723 |
4.499 |
|
Unemployment rate |
10.158 |
10.142 |
10.0 |
9.8 |
9.6 |
Source: IMF Statistics
Le Luxembourg et le pays
Existing conventions and agreements
Non double taxation agreement
In order to promote international economic and financial relations in the interest of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, the Luxembourg government negotiates bilateral agreements for the avoidance of double taxation and prevent fiscal evasion with respect to Taxes on Income and on fortune with third countries.
- Convention from 19.01.2024
Source: Administration des contributions directes
Air Services agreement
Agreement between the Government of the Grand-Duchy of Luxembourg and the Government of the Republic of Chile concerning air services between their respective territories, signed at Luxembourg on 25 February 2002, hereinafter referred to as "Chile-Luxembourg Agreement",
Source: EUR-Lex - Access to European Union Law
Informations supplémentaires
Foreign Trade
The Statec Foreign Trade statistics provide information on the trade of goods - by product and by country. This information is collected respectively through the INTRASTAT declaration and on the basis of customs documents.
You can see the statistics on the website of the Statec.
Contact points in Colombia
Luxembourg is represented by the Ambassade Royale des Pays-Bas à Bogota
Competent post for consular affairs Ambassade du Royaume de Belgique à Bogota
Source: Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Luxembourg
Country risk as defined by Office du Ducroire for Colombia
Ducroire is the only credit insurer covering open account deals in over 200 countries. A rating on a scale from 1 to 7 shows the intensity of the political risk. Category 1 comprises countries with the lowest political risk and category 7 countries with the highest. Macroeconomics experts also assess the repayment climate for all buyers in a country.
Link: Ducroire Office - Country Risk for Colombia